Ether is emerging as the preferred choice for traders looking to amplify returns through leverage, setting it apart from Bitcoin in the race for major cryptocurrencies. While Bitcoin often dominates institutional narratives, Ethereum’s ether (ETH) has become the go-to token for traders seeking to maximize gains using leveraged positions.
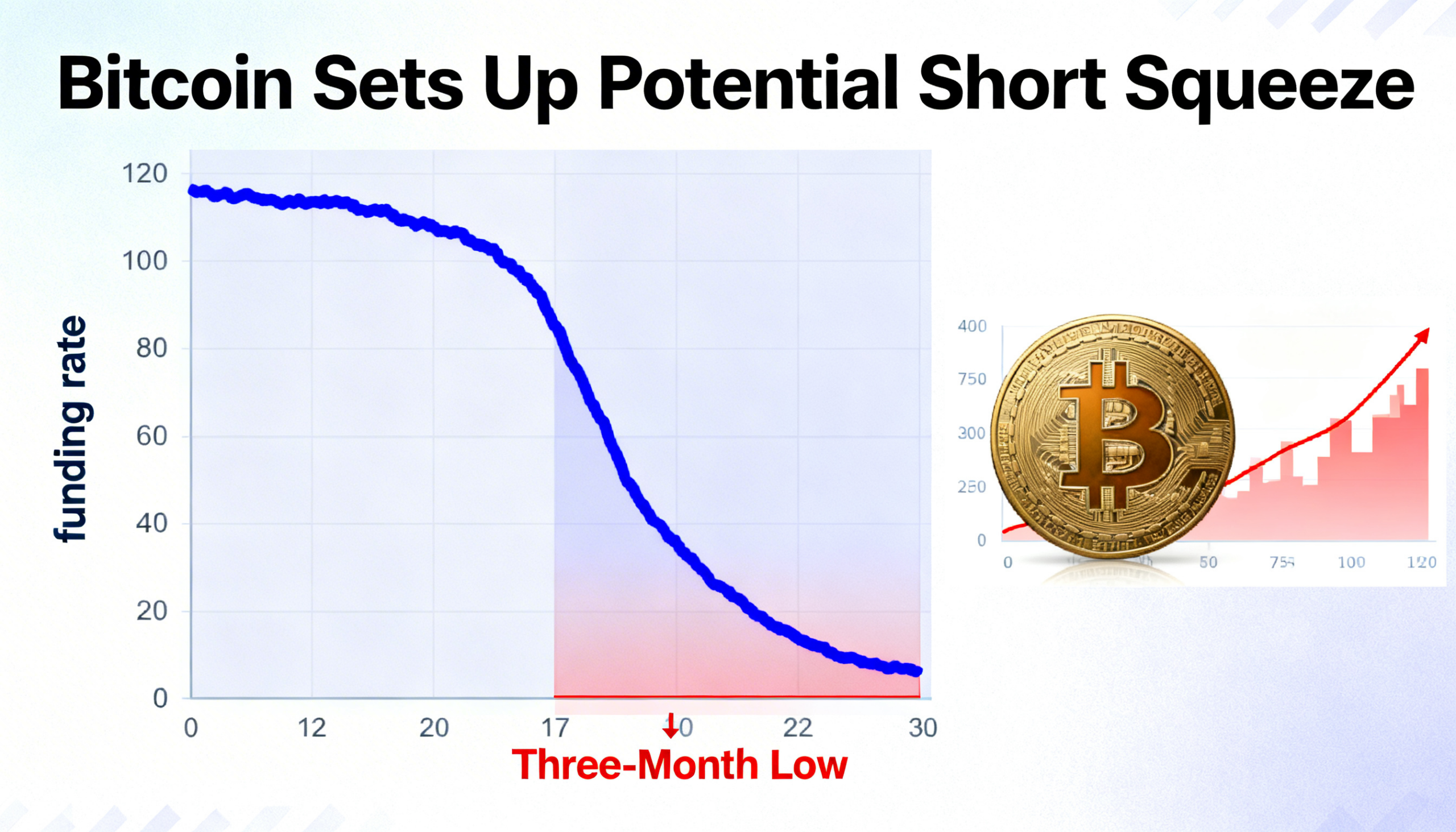
Ether’s leverage ratio, which gauges the extent of leverage employed by traders, reached a new high of 0.57 on Wednesday. This marks a substantial increase from 0.37 at the beginning of Q4 2024, according to data from analytics firm CryptoQuant. The leverage ratio is calculated by dividing the total open interest in both standard futures and perpetual futures contracts by the amount of ETH held in wallets linked to exchanges offering futures trading.
A rising leverage ratio signals that more traders are utilizing leverage, which suggests a growing appetite for risk and speculation in the market. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions in the market with a smaller amount of capital. For example, a leverage ratio of 10:1 would enable a trader to control a $10,000 position with just $1,000 in margin. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses and raises the risk of liquidations, which occur when a trader’s position is forcibly closed due to insufficient margin, often contributing to market volatility.
Ether’s leverage ratio surpassing 0.5 indicates that a significant portion of trading activity in the futures market is driven by leveraged positions, relative to the actual ETH held in exchange wallets. This level of leverage is notably higher than that of Bitcoin, which currently has a leverage ratio of 0.269. Although this is the highest ratio for Bitcoin since early 2023, it remains far below the record high of 0.36 reached in October 2022.
Given these dynamics, it’s not surprising if ether experiences twice the price volatility of Bitcoin in the near future.